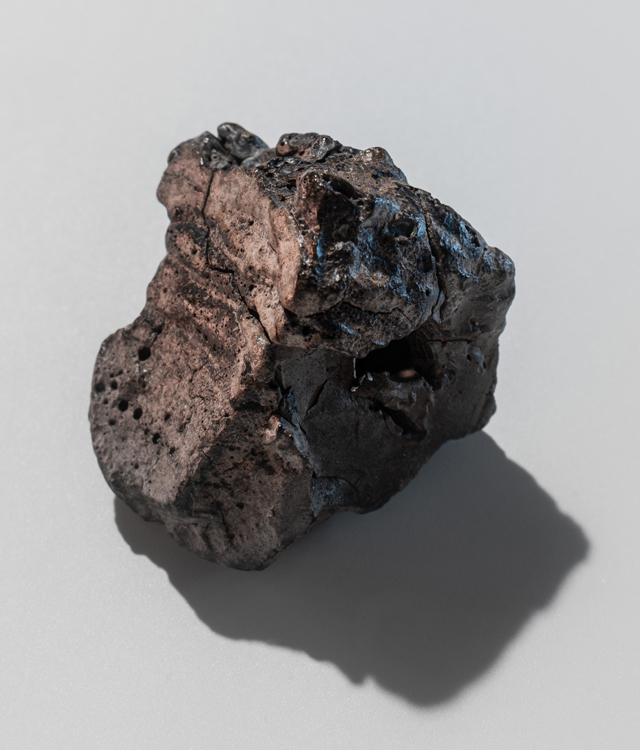
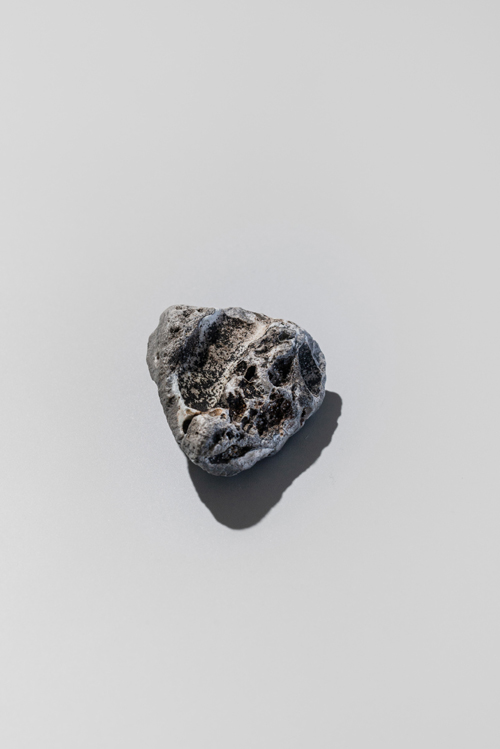
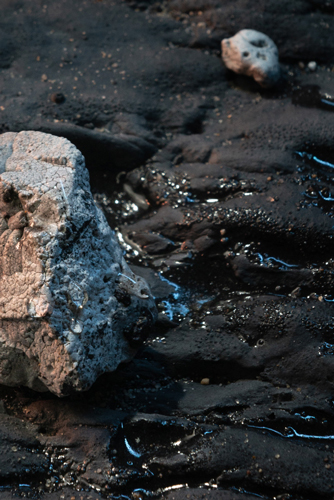| Pollution Type: | Marine litter |
| Material Origin: | Burned or melted plastic that was exposed to marine weather conditions |
| Age: | Partly can be determined based on specific additives (e.g. lead and cadmium) which were often used in the 1950s but became widely regulated in the 1960s |
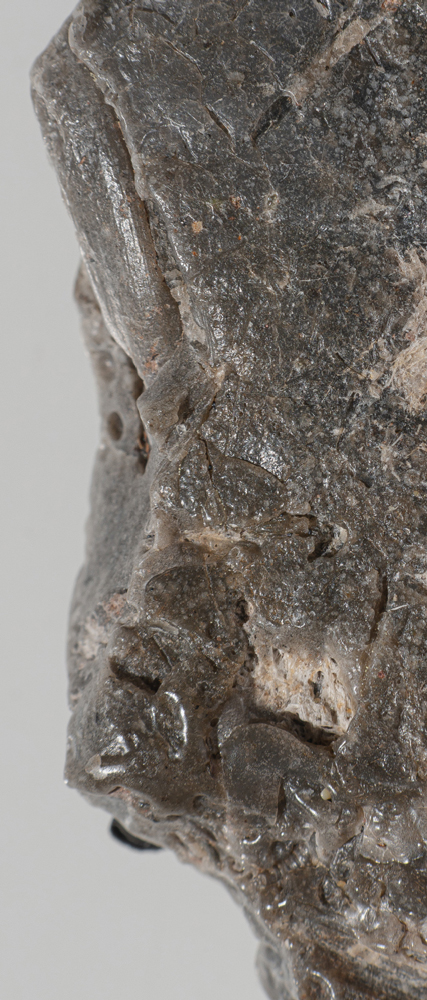
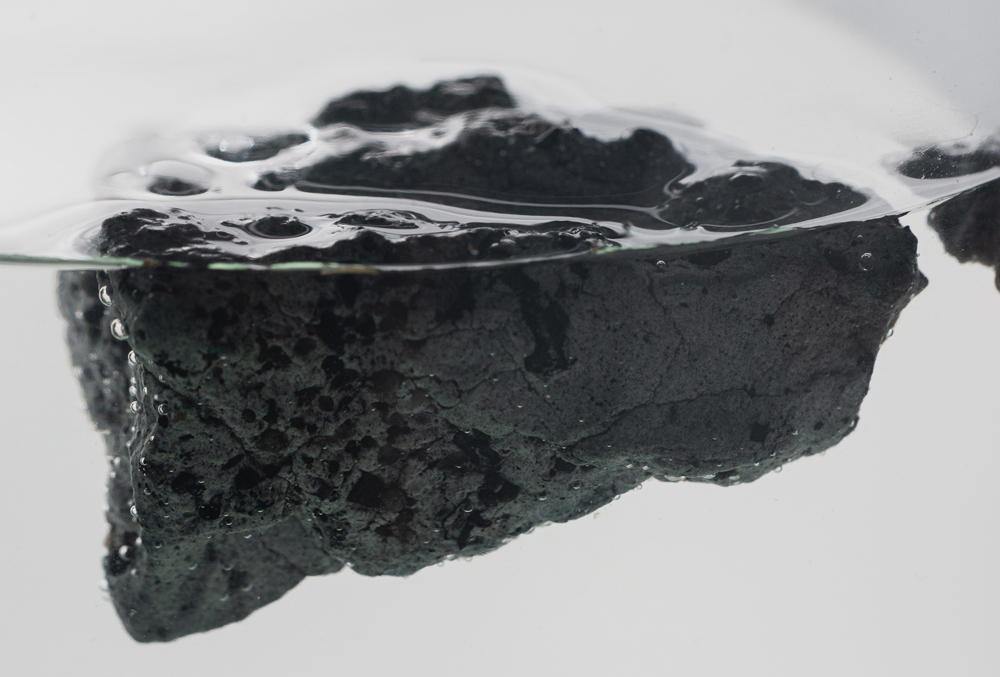
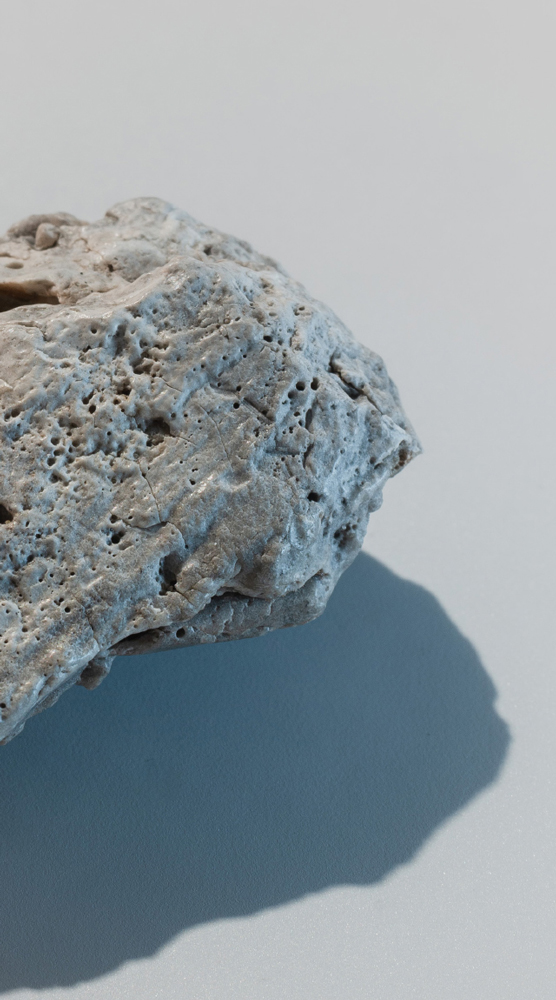
| Shape: | Stone-like appearance that ranges from angular plastiglomerates to more weathered-rounded clasts |
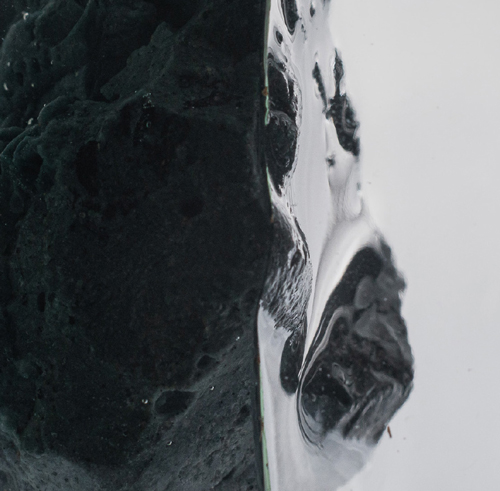
| Colour: | Often exhibits a single and neutral colour (black-charcoal-grey, off-white or brown) with occasional hues of green, blue, pink or yellow |
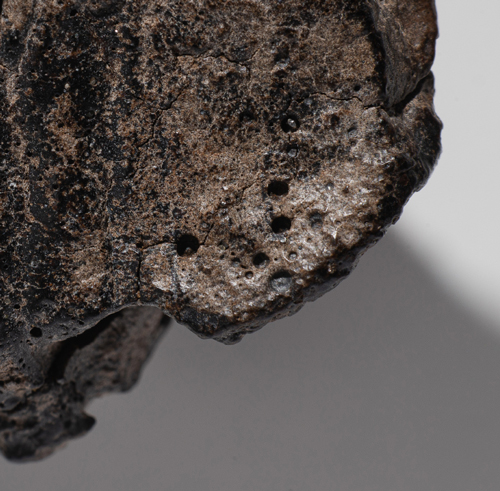
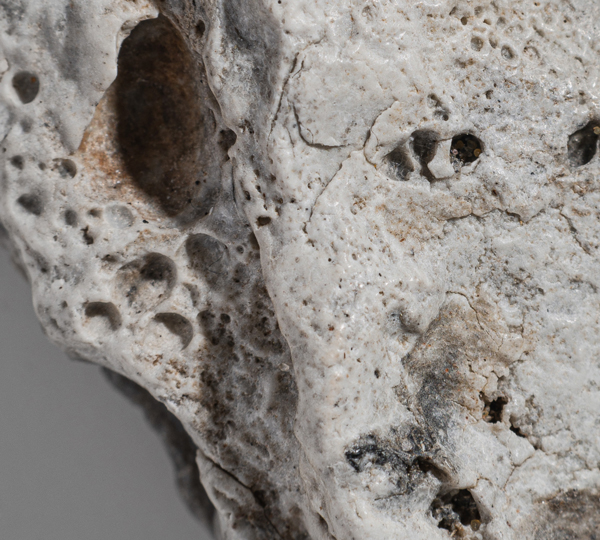
| Texture: | Regular surface features include cracks and fractures as well as pits and cavities |
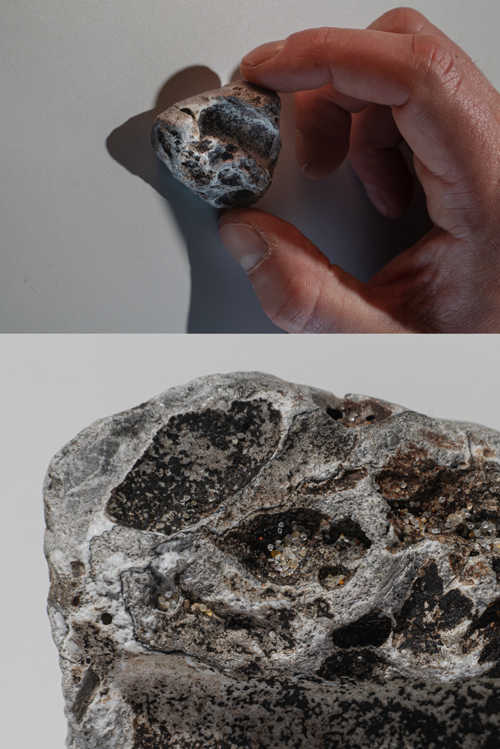
| Size: | Common objects range between20 mm (clasts) and 5 mm (fragments) |
|
Occur- rence: |
Shows a distinctly geogenic appearance in certain coastal areas and can get further distributed by oceanic currents |
|
Buoy- ancy: |
Objects with a polyethylene or polypropylene matrix demonstrate a positive buoyancy |
| Toxic Potential: | Possible hazardous substances include bromine (Br), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr) and lead (Pb) as well as several polymeric additives |
|
Bioavail- ability: |
Partly used as habitat by tubeworms (Spirobranchus triqueter) and algeas |